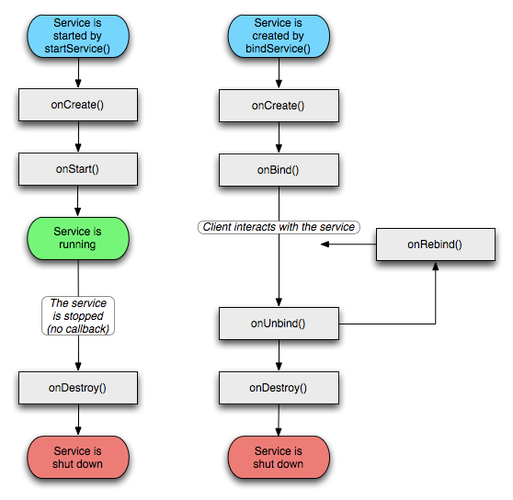
在使用Android开发时,unbindService 方法用于解绑之前绑定的服务,如果未正确处理绑定和解绑逻辑,可能会遇到报错的情况,以下是关于unbindService 报错的详细分析及解决方法:
错误原因分析
在调用unbindService(ServiceConnection connection) 方法前,必须确保服务已经被成功绑定,否则会抛出IllegalArgumentException: Service not registered 异常,这种情况通常发生在以下几种场景中:

未绑定服务直接解绑:在没有调用bindService 的情况下直接调用unbindService。
绑定失败后尝试解绑:虽然调用了bindService,但因为某些原因(如服务不存在、权限不足等)导致绑定失败,之后仍然尝试解绑。
重复解绑:已经成功解绑过一次的服务再次尝试解绑。
解决方案
方案一:使用标志位判断是否已绑定
可以通过一个布尔变量来标记服务是否已经绑定,并在解绑前进行检查。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private MyService.DownloadBinder downloadBinder;
private boolean isBind = false; // 是否绑定服务
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
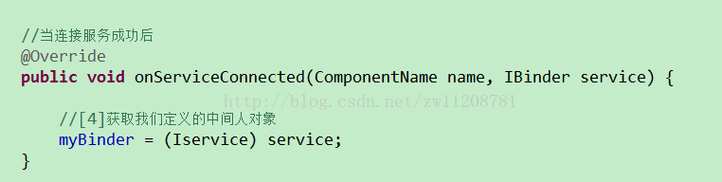
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
downloadBinder = (MyService.DownloadBinder) service;
// 执行相关操作
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// 执行断开连接后的操作
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final Button startService = findViewById(R.id.start_service);
final Button stopService = findViewById(R.id.stop_service);
final Button bindService = findViewById(R.id.bind_service);
final Button unbindService = findViewById(R.id.unbind_service);
startService.setOnClickListener(v > {
Intent startIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
startService(startIntent);
});
stopService.setOnClickListener(v > {
Intent stopIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
stopService(stopIntent);
});
bindService.setOnClickListener(v > {
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
isBind = bindService(bindIntent, connection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); // 绑定服务
});
unbindService.setOnClickListener(v > {
if (isBind) { // 解除绑定前要判断服务是否是绑定状态
unbindService(connection); // 解绑服务
isBind = false;
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "Service not bound", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (isBind) {
unbindService(connection);
isBind = false;
}
}
}方案二:使用反射机制进行判定
在某些情况下,可能需要更复杂的判定逻辑,可以使用反射机制获取系统信息来判断服务是否已绑定,这种方法较为复杂,但在特定情况下非常有用。
try {
Field mPackageInfoField = getBaseContext().getClass().getDeclaredField("mPackageInfo");
mPackageInfoField.setAccessible(true);
Class<?> LoadedApkClass = Class.forName("android.app.LoadedApk");
Field mServicesField = LoadedApkClass.getDeclaredField("mServices");
mServicesField.setAccessible(true);
ArrayMap<Context, Object> mServices = (ArrayMap<Context, Object>) mServicesField.get(mPackageInfoField.get(getBaseContext()));
ArrayMap<Object, Object> map = (ArrayMap<Object, Object>) mServices.get(this);
// 解绑之前进行判定
if (map != null && map.get(this) != null) {
unbindService(this);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}常见问题解答
Q1: 为什么在onDestroy 中调用unbindService 仍然会报错?
A1: 如果在onDestroy 中调用unbindService 仍然报错,可能是因为onDestroy 被多次调用或者在服务未绑定的情况下尝试解绑,建议在解绑前添加标志位检查,并确保只在服务已绑定时调用unbindService,还需确认onDestroy 不会被意外多次调用。
Q2:bindService 和unbindService 使用的ServiceConnection 对象必须是同一个吗?
A2: 是的,bindService 和unbindService 必须使用同一个ServiceConnection 对象,不同的ServiceConnection 对象会导致解绑失败,因为它们的内部状态不一致,确保在整个生命周期中使用同一个ServiceConnection 实例。
unbindService 报错通常是由于在服务未成功绑定或已解绑的情况下再次调用解绑方法所致,通过使用布尔标志位或反射机制进行判定,可以有效地避免此类错误,确保bindService 和unbindService 使用相同的ServiceConnection 对象也是关键。