jsonfromobject
在处理JSON数据时,经常会遇到需要将Python对象转换为JSON格式的情况。jsonfromobject通常指的是使用Python的内置库json 中的dumPS() 方法将一个Python对象转换成JSON字符串,这个过程可能会遇到各种错误和异常,下面将详细探讨这些常见的问题及其解决方法。

1. 基本用法与常见错误
示例代码:
- import json
- data = {"name": "Alice", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}
- json_str = json.dumps(data)
- print(json_str)
可能的错误:
TypeError: Object of type 'XXX' is not JSON serializable
2. 非序列化类型导致的TypeError
问题描述:
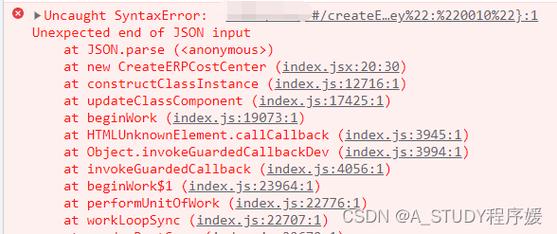
如果尝试序列化的对象包含不可序列化的类型(如自定义类实例、文件对象等),会引发TypeError。
解决方案:
自定义序列化函数。
使用第三方库(如simplejson)。
示例代码:
- class MyClass:
- def __init__(self, name):
- self.name = name
- obj = MyClass("Bob")
- def custom_encoder(obj):
- if isinstance(obj, MyClass):
- return obj.__dict__
- raise TypeError("Object of type {} is not JSON serializable".format(type(obj).__name__))
- json_str = json.dumps(obj, default=custom_encoder)
- print(json_str)
3. 循环引用导致的RecursionError
问题描述:
当对象之间存在循环引用时,默认的json.dumps() 会进入无限递归,导致RecursionError。
解决方案:
使用check_circular 参数来检测循环引用。
自定义序列化函数来处理循环引用。
示例代码:
- import json
- class Node:
- def __init__(self, value):
- self.value = value
- self.next = None
- node1 = Node("Node1")
- node2 = Node("Node2")
- node1.next = node2
- node2.next = node1 # Circular reference
- def custom_encoder(obj):
- if isinstance(obj, Node):
- return {"value": obj.value}
- raise TypeError("Object of type {} is not JSON serializable".format(type(obj).__name__))
- json_str = json.dumps(node1, default=custom_encoder, check_circular=True)
- print(json_str)
4. 编码问题导致的UnicodeEncodeError
问题描述:
当JSON数据中包含非ASCII字符且未指定合适的编码时,会引发UnicodeEncodeError。
解决方案:
明确指定编码方式(如ensure_ascii=False)。
确保所有字符串都是可编码的。
示例代码:
- data = {"name": "Alice", "message": "你好,世界"}
- json_str = json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False)
- print(json_str)
5. 浮点数精度问题
问题描述:
JSON不支持Python中的浮点数精度,可能会导致精度丢失。
解决方案:
使用decimal 模块来处理高精度浮点数。
自定义序列化函数来处理浮点数。
示例代码:
- import decimal
- import json
- data = {"pi": decimal.Decimal("3.141592653589793238462643383")}
- json_str = json.dumps(data, default=lambda o: str(o))
- print(json_str)
相关问答FAQs
Q1: 如何在JSON序列化时保留对象的类型信息?
A1: 可以通过自定义序列化函数来实现,在序列化过程中,可以添加额外的字段来存储对象的类型信息。
- class MyClass:
- def __init__(self, name):
- self.name = name
- def custom_encoder(obj):
- if isinstance(obj, MyClass):
- return {'__type__': 'MyClass', 'name': obj.name}
- raise TypeError("Object of type {} is not JSON serializable".format(type(obj).__name__))
- obj = MyClass("Bob")
- json_str = json.dumps(obj, default=custom_encoder)
- print(json_str) # 输出: {"__type": "MyClass", "name": "Bob"}
Q2: 如何处理JSON序列化时的日期时间对象?
A2: Python的datetime 模块提供了对日期和时间的支持,但默认情况下,json.dumps() 无法直接序列化datetime 对象,可以通过自定义序列化函数来处理日期时间对象。
- from datetime import datetime
- import json
- def datetime_encoder(obj):
- if isinstance(obj, datetime):
- return obj.isoformat()
- raise TypeError("Object of type {} is not JSON serializable".format(type(obj).__name__))
- now = datetime.now()
- json_str = json.dumps({"current_time": now}, default=datetime_encoder)
- print(json_str) # 输出: {"current_time": "20240717T12:34:56.789012"}