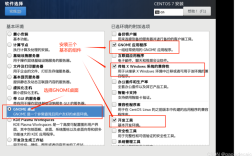
Centos (Community ENTerprise Operating System) is a widely used Linux distribution that has gained popularity among system administrators and developers due to its stability, reliability, and compatibility with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). CentOS is an opensource operating system based on the source code of RHEL, but it is not officially supported by Red Hat. Instead, it is maintained by the CentOS Project, which consists of volunteers and contributors from around the world.
CentOS offers two main streams: CentOS Linux and CentOS Stream. CentOS Linux is designed for production environments, providing a stable and secure platform for running applications and services. It is based on the latest stable release of RHEL and receives security updates and bug fixes from Red Hat. CentOS Stream, on the other hand, is a rolling release that tracks the development cycle of RHEL. It provides users with access to the latest features and improvements as they become available, but it may also include bugs and unstable components.
One of the key advantages of using CentOS is its compatibility with RHEL. Since CentOS is based on the same source code as RHEL, applications and scripts developed for RHEL can usually run without any modifications on CentOS. This makes it easier for organizations to transition from RHEL to CentOS or vice versa, reducing the need for retraining or rewriting code.
CentOS also supports a wide range of hardware architectures, including x86_64 (64bit), i386 (32bit), ARM, and more. This flexibility allows users to deploy CentOS on various types of systems, from servers and workstations to embedded devices and cloud instances.
In terms of package management, CentOS uses the YUM (Yellowdog Updater, Modified) package manager by default. YUM is a powerful tool that automates the process of installing, updating, and managing software packages on CentOS systems. It relies on repositories, which are collections of software packages hosted on remote servers. By default, CentOS includes several official repositories that provide access to a large number of packages, but users can also add custom repositories if needed.
Another important aspect of CentOS is its focus on security. The CentOS Project regularly releases security updates and patches for the operating system, ensuring that users have access to the latest protections against vulnerabilities and exploits. In addition, CentOS supports various security features such as SELinux (SecurityEnhanced Linux), which provides mandatory access control policies to enhance system security.
CentOS also has a strong community behind it, with many resources available for learning and troubleshooting. The CentOS Official Website (httPS://www.centos.org/) serves as the primary source of information for the project, including documentation, news, and download links. The website also hosts forums and mailing lists where users can ask questions, share experiences, and collaborate on solving problems.
Overall, CentOS is a robust and flexible Linux distribution that offers a costeffective alternative to commercial operating systems like RHEL. Its compatibility with RHEL, extensive hardware support, powerful package management tools, and strong security features make it a popular choice for both individual users and enterprises.