在使用Spring框架进行开发时,@Autowired注解是依赖注入的核心工具之一,但许多开发者在实际编码中常遇到因该注解引发的报错问题,本文将深入分析常见错误场景,并提供具体解决方案,帮助开发者规避陷阱,提升代码质量。
一、空指针异常(NullPointerException)
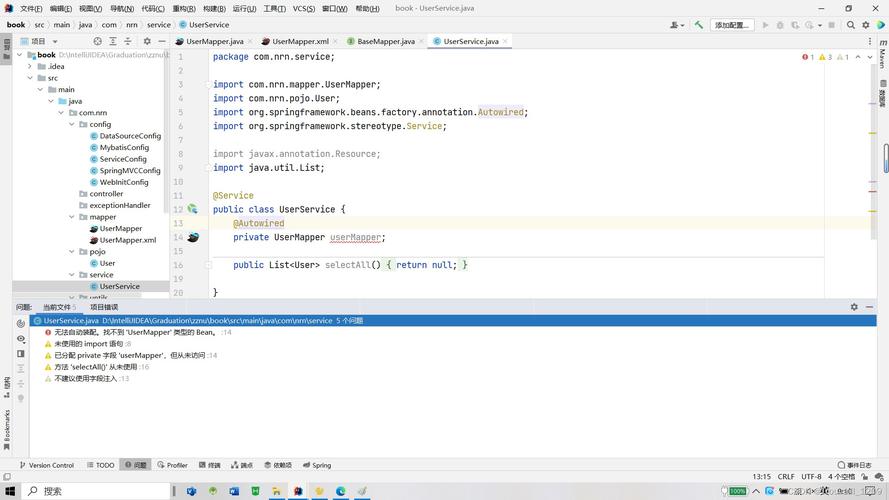
当试图通过@Autowired注入的Bean对象调用方法时,若控制台抛出空指针异常,通常由以下两种原因导致:
1. Bean未被Spring容器管理
问题根源
未在类上添加@Component、@Service等注解,导致Spring无法扫描并实例化该对象。
示例代码
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository; // 此处注入失败
}解决方案
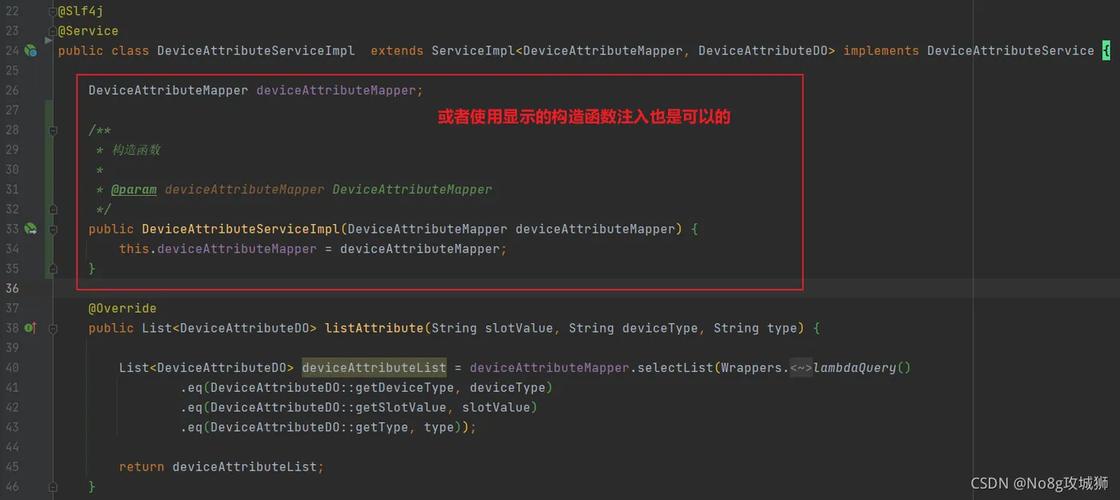
添加类级注解,如@Service:
@Service
public class UserService {
// 正确注入
}2. 包扫描路径配置错误
排查步骤
检查启动类或配置类中的@ComponentScan注解是否包含目标类的包路径。
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example")
public class Application { }**二、多个Bean冲突导致注入失败
当同一接口存在多个实现类时,直接使用@Autowired会触发NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException异常。
场景复现
public interface PaymentService {}
@Service
public class AlipayService implements PaymentService {}
@Service
public class WechatPayService implements PaymentService {}
// 注入时发生冲突
@Autowired
private PaymentService paymentService;解决方案
使用@Qualifier明确指定Bean名称
@Autowired
@Qualifier("alipayService")
private PaymentService paymentService;在实现类中定义优先级
通过@Primary注解标记默认注入的Bean:
@Service
@Primary
public class AlipayService implements PaymentService {}**三、作用域(Scope)不匹配
若被注入的Bean作用域与当前上下文不兼容,例如将prototype作用域的Bean注入到singleton作用域的类中,可能引发意外行为。
典型错误示例
@Service
@Scope("prototype")
public class PrototypeBean {}
@Service
public class SingletonBean {
@Autowired
private PrototypeBean prototypeBean; // 每次获取的实例可能不符合预期
}修正方案
通过ApplicationContext动态获取Bean
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public void usePrototypeBean() {
PrototypeBean bean = applicationContext.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
}使用@Lookup注解(仅限方法级注入)
@Lookup
public PrototypeBean getPrototypeBean() {
return null; // 由Spring代理实现
}**四、循环依赖问题
当两个或多个Bean相互依赖时,Spring可能无法完成初始化,抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException。
案例场景
@Service
public class ServiceA {
@Autowired
private ServiceB serviceB;
}
@Service
public class ServiceB {
@Autowired
private ServiceA serviceA;
}解决方法
重构代码结构
提取公共逻辑到第三个类中,打破循环链。
使用Setter注入替代字段注入
@Service
public class ServiceA {
private ServiceB serviceB;
@Autowired
public void setServiceB(ServiceB serviceB) {
this.serviceB = serviceB;
}
}启用@Lazy延迟加载
@Autowired @Lazy private ServiceB serviceB;
**五、静态字段无法直接注入
@Autowired无法直接作用于静态变量,因其违背依赖注入的设计原则。
错误写法
@Autowired private static UserService userService; // 注入失败
正确实践
通过Setter方法间接赋值
private static UserService userService;
@Autowired
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
MyClass.userService = userService;
}避免静态依赖
优先考虑单例模式或工具类封装,而非强制使用静态字段。
**最佳实践建议
1、优先使用构造器注入
Spring官方推荐通过构造器显式声明依赖关系,避免字段注入的隐藏风险:
@Service
public class OrderService {
private final PaymentService paymentService;
@Autowired
public OrderService(PaymentService paymentService) {
this.paymentService = paymentService;
}
}2、定期检查依赖关系
使用IDE的依赖分析工具(如IntelliJ的"Diagram"功能)可视化Bean依赖,提前发现潜在问题。
3、单元测试验证
编写集成测试时,结合@SpringBootTest注解确保Bean注入逻辑正确。
在实际开发中,@Autowired报错往往源于对Spring机制的理解偏差,通过精确控制Bean的生命周期、合理规划代码结构,并结合框架特性灵活调整注入方式,能够显著降低错误发生率,作为开发者,持续关注Spring官方文档更新,并参与技术社区讨论,是提升问题解决效率的关键路径。